Left vs Right Hemisphere: Myths & Facts
Left vs Right Hemisphere: Myths & Facts
The human brain is divided into two halves — the left and right hemispheres — each connected by a thick bundle of nerve fibers called the **corpus callosum**. For decades, people have believed that the left side is logical and analytical while the right side is creative and emotional. While this idea sounds appealing, neuroscience tells a more accurate story: both hemispheres share responsibilities and constantly work together to shape our perception, language, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
Understanding the Two Hemispheres
The left and right hemispheres are mirror images in structure but not identical in function. Each controls the opposite side of the body — the left hemisphere manages the right side, and the right hemisphere controls the left. This cross-wiring ensures coordination and balance in movement and perception.
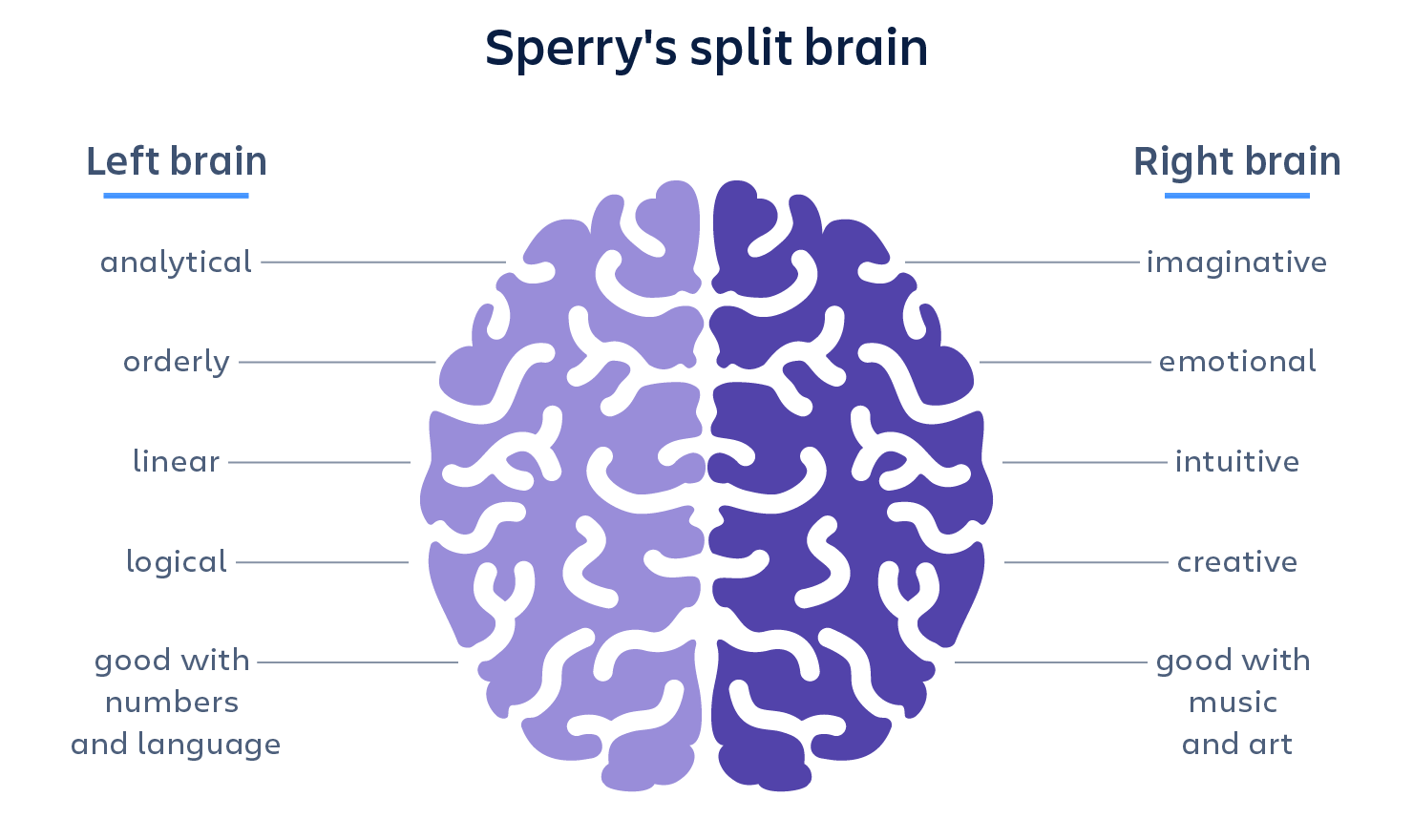
The **left hemisphere** tends to specialize in tasks that require order, logic, and detail. It’s heavily involved in language, speech, mathematical reasoning, and sequential processing. The **right hemisphere**, in contrast, excels in recognizing patterns, visual-spatial awareness, emotion, and creativity. It helps interpret facial expressions, appreciate music, and understand metaphors. However, both sides constantly communicate through the corpus callosum to create a unified experience.
The Origin of the Left- and Right-Brain Myth
The “left-brained” versus “right-brained” theory emerged from research in the 1960s, when scientists studied patients who had their corpus callosum severed to treat epilepsy. They discovered that certain functions seemed dominant in one hemisphere. Over time, this led to the misconception that people primarily use one side of the brain more than the other.
In reality, brain imaging studies show that almost every activity — from writing poetry to solving equations — involves both hemispheres working together. The idea of being entirely “left-brained” or “right-brained” is a myth; what matters is how efficiently the two halves communicate.
How the Hemispheres Collaborate
Everyday tasks require seamless cooperation. When you speak, the left hemisphere formulates grammar and vocabulary, while the right hemisphere interprets tone and emotional meaning. When you listen to music, the right hemisphere appreciates melody and harmony, while the left tracks rhythm and structure.
Even decision-making uses both sides: the right hemisphere assesses context and intuition, while the left analyzes facts and logic. This partnership allows for well-rounded thinking — blending emotion and reason, creativity and precision.
Language, Art, and Emotion
Language offers one of the clearest examples of hemispheric specialization. **Broca’s area** and **Wernicke’s area**, located in the left hemisphere, handle speech production and comprehension. However, understanding humor, sarcasm, and tone relies on the right hemisphere. Without it, speech would sound robotic and emotionless.
In creative arts, the right hemisphere is active in visual imagination and spatial design, but the left contributes to technique, timing, and structure. Together they enable painters, musicians, and writers to balance inspiration with discipline.
Brain Plasticity and Adaptation
Another misconception is that the hemispheres cannot adapt. In fact, the brain is remarkably flexible. After injury, regions from the opposite hemisphere can often take over lost functions — a phenomenon known as **neuroplasticity**. For instance, if the left hemisphere’s language centers are damaged early in life, the right hemisphere can sometimes reorganize to support speech and comprehension.
This adaptability shows that the hemispheres are not rigidly fixed in their duties but part of an interconnected network capable of growth and compensation.
Everyday Examples of Hemisphere Cooperation
Consider writing a story. The left hemisphere chooses words, structures sentences, and maintains logic, while the right hemisphere imagines scenes, emotions, and rhythm. Similarly, when you drive a car, your left hemisphere processes rules and signals, while your right hemisphere handles spatial awareness and quick reactions.
Teamwork between hemispheres is what makes complex human behavior possible — from cooking to dancing to solving puzzles. The more you engage both logic and creativity, the stronger this connection becomes.
Balancing Both Sides of the Brain
There’s no need to “train” just one side of your brain. Instead, focus on activities that engage both hemispheres together. Learning a new language, playing a musical instrument, solving math problems, or practicing art all stimulate neural connections across the corpus callosum. Physical exercise and mindfulness also enhance hemispheric coordination by improving blood flow and focus.
A balanced brain — one that values both precision and imagination — leads to better learning, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Key Takeaways
- The two hemispheres: The left handles logic, language, and analysis; the right manages creativity, emotion, and spatial awareness.
- Myth vs fact: People are not “left-brained” or “right-brained.” Both hemispheres constantly collaborate through the corpus callosum.
- Example: When telling a story, the left hemisphere structures sentences while the right adds emotion and tone.
- Cooperation: Every task — reading, art, music, decision-making — relies on both hemispheres working in sync.
- Plasticity: The brain can adapt after injury, with one hemisphere compensating for the other when needed.
- Healthy habits: Engage in diverse activities like music, language learning, puzzles, and exercise to strengthen inter-hemispheric communication.
- Analogy: The hemispheres are like two musicians in a duet — one providing rhythm, the other melody — creating harmony only when they play together.
- Awareness: True intelligence and creativity come from balance, not dominance, between the left and right sides of the brain.
Disclaimer: These pages are for education only and do not replace professional advice.